|
Wizard sizing / Inertia calculation
|
Inertia calculation
From dimensions and mass or density of a rigidity , you can calculate the moment of inertia.
When data were load with Data load/ delete or Machine information, or the moment of inertia already calculated, parameters that were already finished setting are displayed.
[Operation Procedure]
- Select a rigid body.
When the target rigid is not displayed, click a "Page Move button".
- Enter data in the data input column.
When there are blanks and the input except a number, it cannot calculate.
If necessary, click "Mass Input" to switch the input column.
- Click "Calculate".
- When "OK" is clicked, it returns to the Machine information and displays the calculation result.
When "Cancel" is clicked, it returns to the Machine information after deleting input data.
[Screen Structure]
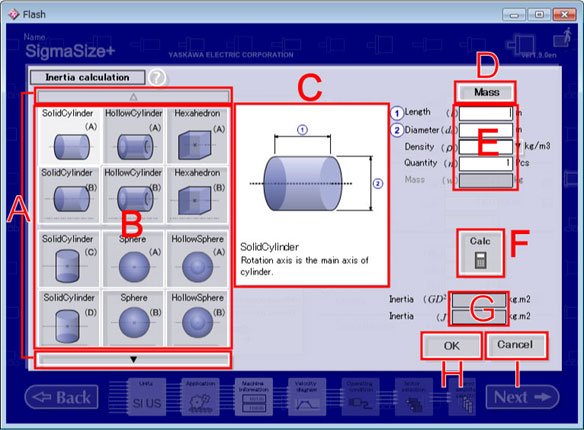
Inertia Calculation Screen (Solid Cylinder [A])
Page Move button
Scroll up or down of a rigid display list.
Button clicking does not do anything in the mask display mode pick.
Rigidity button
In initial state, a solid cylinder (A) is selected.
Select Rigidity for the calculation of inertia
There are 16 kinds of bodies shown in the below table.
Rigidity Preview
The rigidity selected is zoomed in.
Mass Input Button
You can select in either of the mass input method and a mass calculation method.
When you have known the rigidity mass, you select the mass input method and input the column of mass.
Data Input Column
Input the required data for the inertia calculation.
The number of maximum input beams of each input column is 12 figures(include such as a mark and a decimal point).
Example
Possible :1.0,-1.0,1.2345678912,-1.234567891,1.0e+100 etc.
Impossible;:1.00000000000,-1000000000,1.23456789123,1.000000e+001 etc.
Calculation button
Calculates inertia.
Data Output Column
The calculated result is displayed.
The inertia of an engineering unit GD2 is calculated as GD2 = 4 J.
OK button
Returns to the Machine information and displays the calculation Ineartia(J).
Cancel button
Returns to the Machine information detailed Machine Information, and then deletes the selected rigid body and input data.
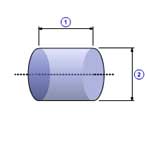
Solid cylinder(A)
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Diameter( dO ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l d02 / 4
J =
n m d02 / 8
[
Back]
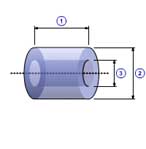
Hollow cylinder(A)
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Major diameter( d0 ) |
| 3 | Minor diameter( d1 ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l (
d02 -
d12 ) / 4
J =
n m (
d02 +
d12 ) / 8
[
Back]
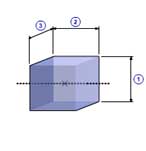
Rectangular solid(A)
|
1 |
Height( b ) |
| 2 | Length( t ) |
| 3 | Width( c ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
ρ b c t
J =
n m (
b2 +
c2 ) / 12
[
Back]
Solid cylinder(B)
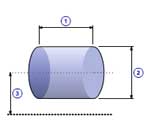
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Diameter( d0 ) |
| 3 | Distance( d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l d02 / 4
J =
n (
md02 / 8 +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
Hollow cylinder(B)
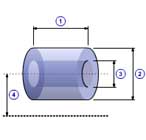
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Major diameter( d0 ) |
| 3 | Minor diameter( d1 ) |
| 4 | Distance( d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l (
d02 -
d12 ) / 4
J =
n (
m d02 / 8 +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
Rectangular solid(B)
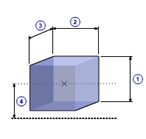
|
1 |
Height(b ) |
| 2 | Length(t ) |
| 3 | Width(c ) |
| 4 | Distance(d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
ρ b c t
J =
n (
m (
b2 +
c2 ) / 12 +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
Solid cylinder(C)
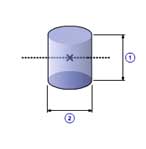
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Diameter( d0 ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l d02 / 4
J =
n m (
d02 / 16 +
l 2 / 12 )
[
Back]
Sphere(A)
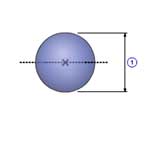
|
1 |
Diameter( d0 ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ d03 / 6
J =
n m d02 / 10
[
Back]
Hollow sphere(A)
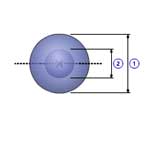
|
1 |
Major diameter( d0 ) |
| 2 | Minor diameter( d1 ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ (
d03 -
d13 ) / 6
J =
n m (
d05 -
d13 ) / (
d03 -
d13 ) / 10
[
Back]
Solid cylinder(D)
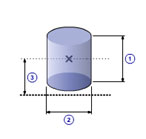
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Diameter( d0 ) |
| 3 | Distance( d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l d02 / 4
J =
n (
m (
d02 / 16 +
l 2 / 12 ) +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
Sphere(B)
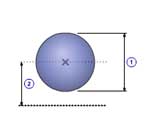
|
1 |
Diameter( d0 ) |
| 2 | Distance( d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ d03 / 6
J =
n (
m d02 / 10 +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
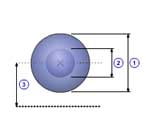
Hollow sphere(B)
|
1 |
Major diameter( d0 ) |
| 2 | Minor diameter( d1 ) |
| 3 | Distance( d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ (
d03 -
d13 ) / 6
J =
n (
m (
d05 -
d13 ) / (
d03 -
d13 ) / 10 +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
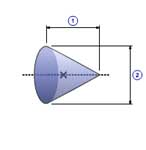
Cone(A)
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Diameter( d0 ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l d02 / 12
J =
n 3 m d02 / 40
[
Back]
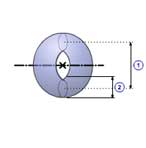
Torus(A)
|
1 |
Major radius( r0 ) |
| 2 | Minor radius( r1 ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π 2ρ r0 r12 / 4
J =
n m ( 4
r02 + 3
r12 ) / 16
[
Back]
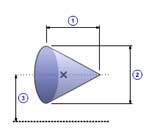
Cone(B)
|
1 |
Length( l ) |
| 2 | Diameter( d0 ) |
| 3 | Distance( d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π ρ l d02 / 12
J =
n ( 3
m d02 / 40 +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
Cone(B)
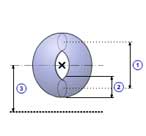
|
1 |
Major radius( r0 ) |
| 2 | Minor radius( r1 ) |
| 3 | Distance( d ) |
| Density( ρ ) |
| Quantity( n ) |
| Mass( m ) |
m =
π 2ρ r0 r12 / 4
J =
n (
m ( 4
r02 + 3
r12 ) / 16 +
m d 2 )
[
Back]
















